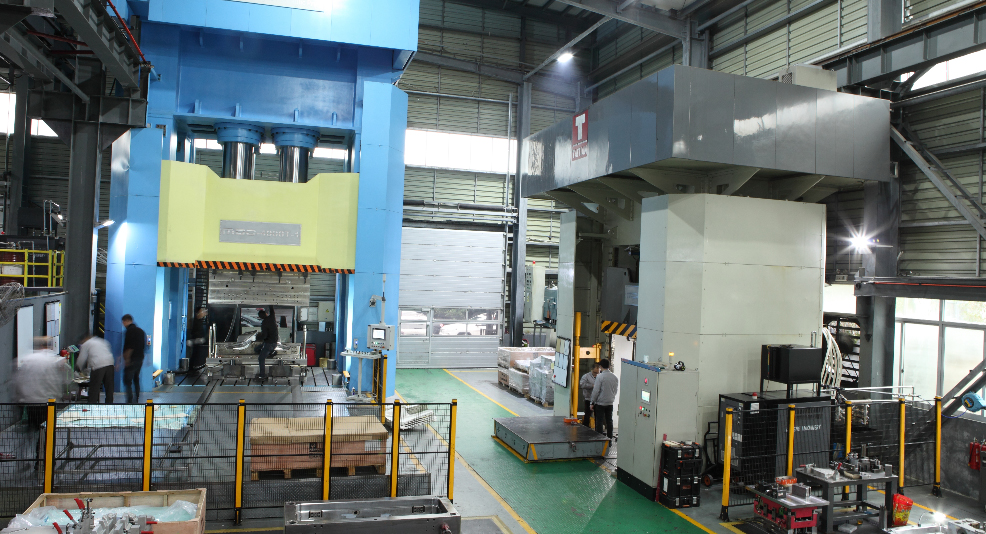
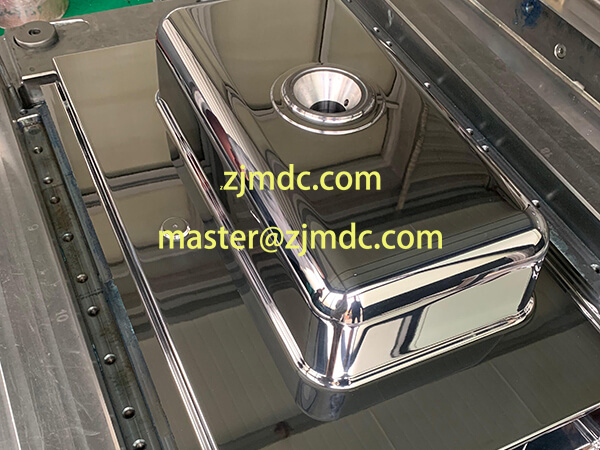
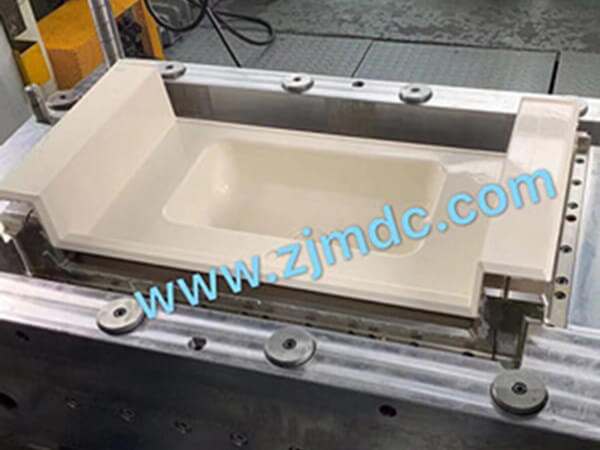
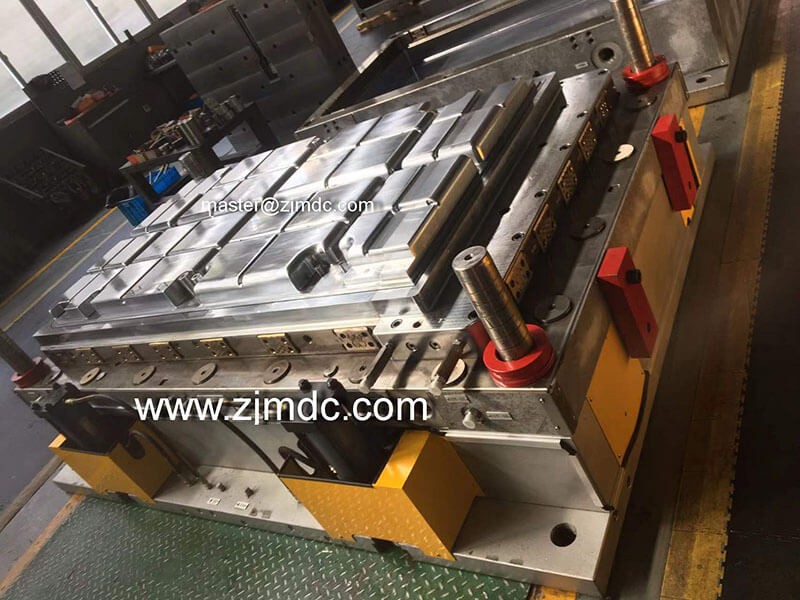
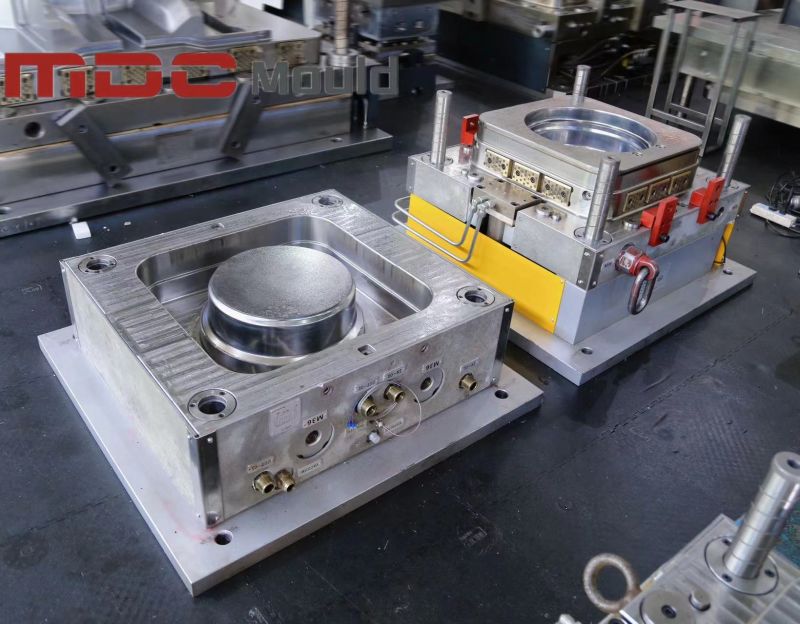
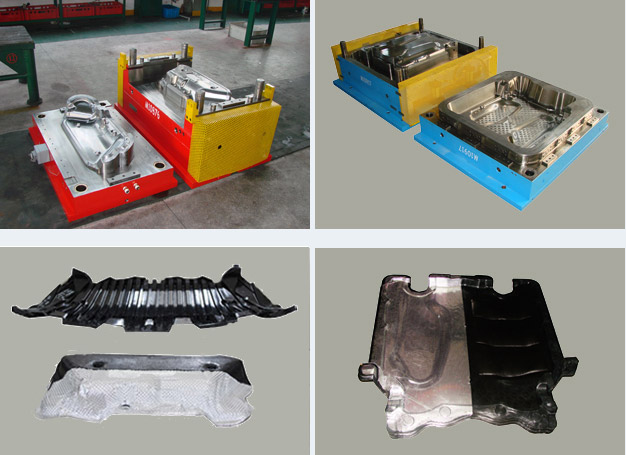
In the field of compression molding for composite materials, precise temperature control is the foundation of product stability and mold longevity. Among the most critical yet often underestimated steps is preheating the compression mold. At MDC Mould, this process is considered a key factor in achieving high-performance results for SMC, BMC, and carbon fiber components.
Why Preheating Compression Molds Matters
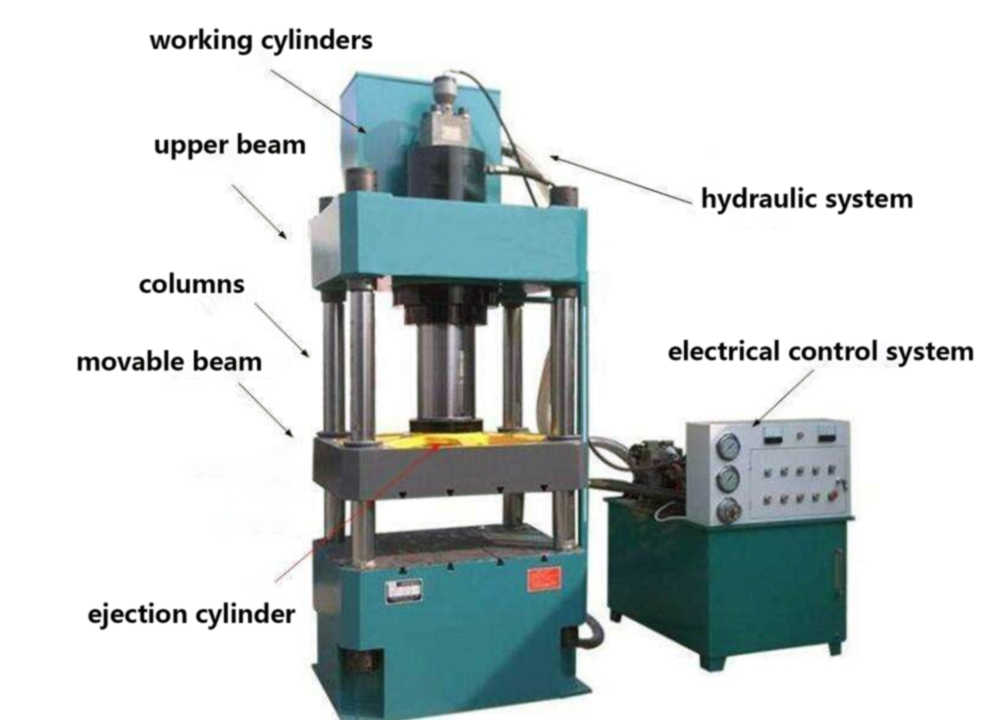
The compression molding process involves applying heat and pressure to a composite charge within a mold cavity. If the mold is not adequately preheated before production, material flow becomes unstable, leading to defects such as voids, incomplete curing, or warping. MDC’s engineering experience shows that maintaining precise mold temperature from the first cycle is vital to achieving dimensional consistency and optimal resin cross-linking.
- Ensures even material flow and uniform curing;
- Prevents air entrapment and surface imperfections;
- Improves resin-fiber bonding strength;
- Extends mold life by reducing thermal stress shock.
The Science of Mold Preheating
Different composite systems—such as SMC (Sheet Molding Compound), BMC (Bulk Molding Compound), and carbon fiber-reinforced composites—require specific mold temperatures for optimal molding conditions. Typically, SMC and BMC molds operate between 130°C and 160°C, while aerospace-grade carbon fiber applications may require preheating up to 180°C or beyond.
MDC’s hot press molds integrate precision heating channels and temperature sensors to maintain balanced thermal distribution across large and complex cavity surfaces. This uniformity minimizes localized hot spots and ensures consistent material flow during the entire molding cycle.
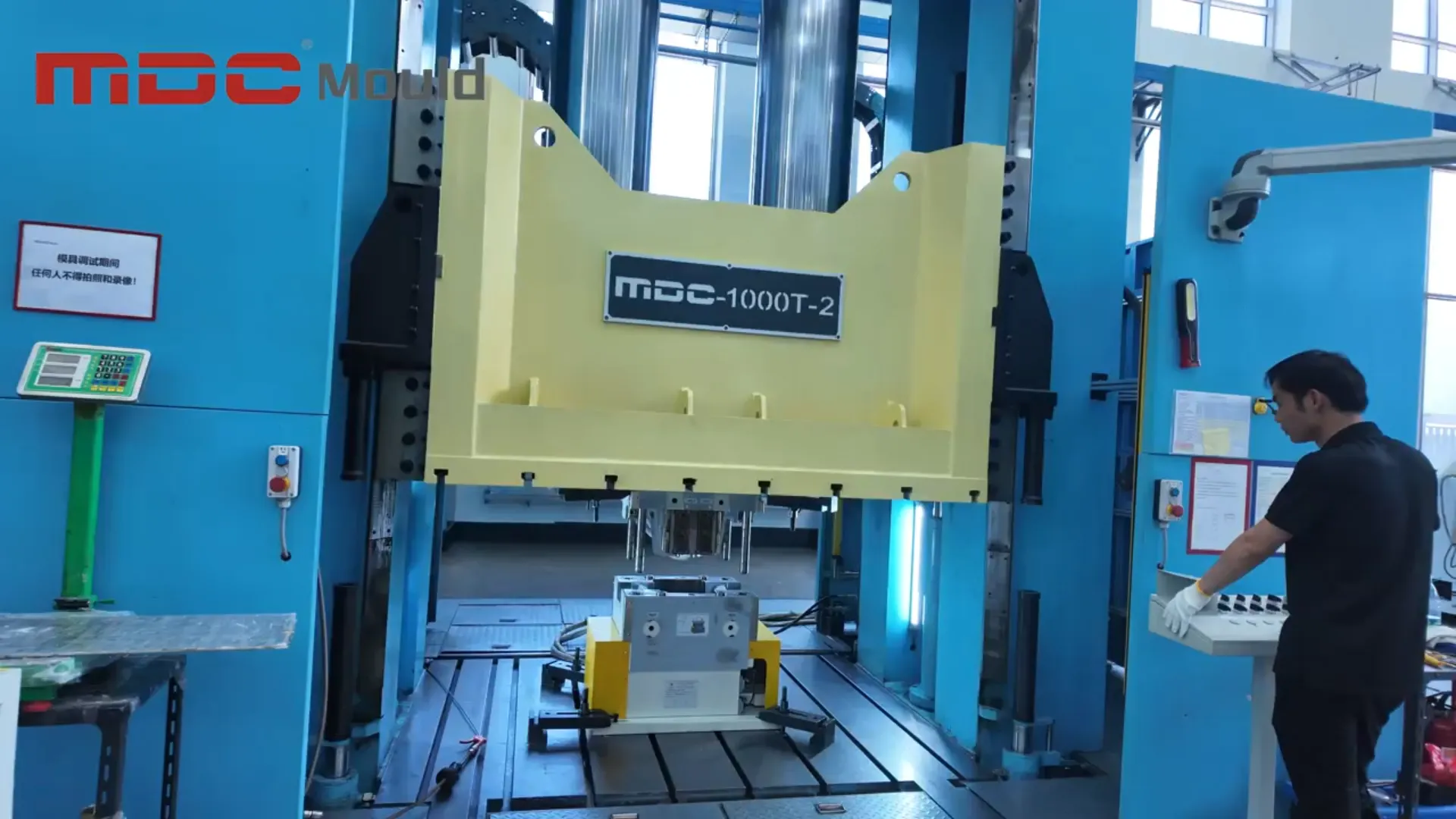

Mold Preheating Methods Used at MDC
MDC utilizes a range of preheating systems according to material type and production scale:
- Electric heating systems – offering precise and independent control for each mold zone;
- Oil heating systems – providing steady, even temperature for large or multi-cavity molds;
- Steam and hot-water preheating – suitable for low to mid-temperature composite applications;
- Integrated PID control – ensuring real-time temperature regulation and safety monitoring.
Through advanced mold design and thermal simulation, MDC engineers ensure that heat transfer efficiency is maximized while minimizing energy loss, resulting in shorter preheating times and stable production.
Benefits of Proper Mold Preheating
Preheating a compression mold properly has direct impact on final product performance and overall production efficiency. Benefits include:
- Enhanced surface quality – reduced flow marks and resin-rich zones;
- Stable cycle times – consistent curing rates and dimensional control;
- Increased mechanical properties – improved tensile and flexural strength;
- Reduced energy waste – improved heating efficiency and fewer startup defects.
MDC’s Engineering Approach
At MDC, every compression mould is designed with precision and long-term durability in mind. The company integrates thermal analysis and simulation into its design phase, allowing engineers to predict heat flow, temperature gradients, and curing uniformity. This predictive approach ensures that each mold delivers stable performance even under continuous production conditions.
MDC’s preheating solutions are particularly beneficial for:
- SMC auto parts such as bumpers, battery covers, and trunk boards;
- BMC electrical components requiring high dimensional precision;
- Carbon fiber structural parts in aerospace and industrial sectors.
Future Trends in Compression Molding Temperature Control
As composite manufacturing advances, mold temperature systems are becoming increasingly intelligent. MDC is developing new-generation preheating and thermal management solutions featuring real-time data acquisition, energy-efficient heating technologies, and smart temperature regulation to further enhance product quality and sustainability.
Conclusion
Preheating is not just a preparatory step — it is a foundation for precision molding. Through continuous innovation in compression mold design and temperature control technology, MDC Mould empowers manufacturers to achieve higher efficiency, stability, and quality in composite production. MDC remains committed to advancing composite mold engineering for a lighter, stronger, and more sustainable future.